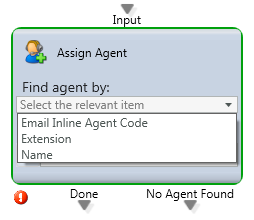
Assign Agent
Media Type: All
Purpose: Routing decision to assign an interaction to a particular agent based upon their name, extension, or specific attribute.
Attributes:
- Email Inline Agent Code – Entered at the bottom of the email response so that when the correspondence continues, the code is used to assign the email to the same agent
- Extension (###)
- Name (First Name, Last Name)
Output Legs:
- Done: An agent the selected Attribute
- No Agent Found: No agent matched the selected Attribute
Common Use Case:
- Last Agent Routing: Route an interaction to the agent they last spoke with using the “Assign Agent by Name” Attribute that would be compared to a Flow Variable that contains the “Last Handling Agent” Property from the “Get Contact History Data” Activity.
- Preferred Agent Routing: Route an interaction to a preferred agent using the “Assign Agent by Name” Attribute that would be compared to a CRM Property that contains the agent’s name
Branch
Media Type: All
Purpose: Used to make a routing decision based upon any data elements available. This is the most dynamic node in ECS and can be used to solve a majority of routing needs.
Filter Attributes:
- Match or Mismatch – You can set each leg/filter to only activate once the specified criteria is a match or a mismatch.
- Any or All– This indicates if the leg/filter will activate when any of the conditions being met or only when all of the conditions are met.
- Conditions
- Contains
- Greater Than
- Greater Than or Equal
- Is
- Is Not
- Less Than
- Less Than or Equal
- Context
- Property, Flow Variable or Business Process – The context for which the call or leg will be active.
Output Legs: The leg(s) for a Brach node is dynamic. The number of legs is dependent on the number of filters created.
Common Use Case:
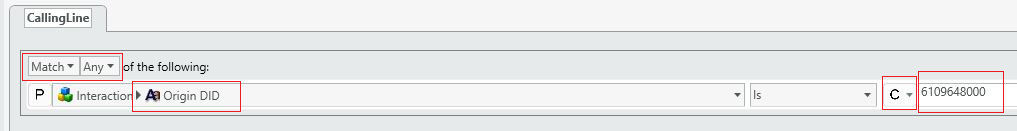
- Special treatment for one or more incoming phone numbers: Let’s say you want to route calls originating from 6109648000 to a specific greeting, menu or business process. You would create the following branch filter to achieve this.
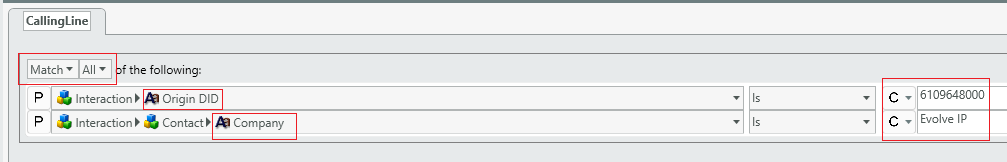
- Routing a specific number & CRM value: Now let’s say you want to achieve the above however only when the Company is also Evolve IP.
- Routing based upon the Interaction Types: You can also use the Branch node to route based upon the Interaction Type.
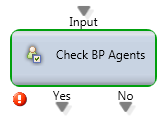
Check BP Agents
Media Type: All
Purpose:
Routing decision based upon agent availability in the queue.
Output Legs:
- Yes: There is at least 1 agent in “Ready” state. Agents in all other states (Break, Handle Outgoing, Back Office, etc.) are ignored.
- No: There are no agents in the “Ready” state.
Common Use Case:
This node is used in a scenario when the routing logic needs to ensure an Interaction will be presented to a Ready agent.
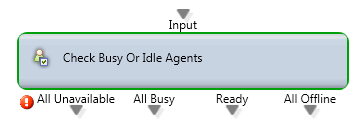
Check Busy or Idle Agents
Media Type: All
Purpose: Routing decision based upon agent availability in the queue.
Output Legs:
- All Unavailable: All agents are in the following states “Break, Offline, Handle Outgoing, and Back Office”.
- All Busy: All agents are Busy handling Interactions.
- Ready: There is at least 1 agent in “Ready” state.
- All Offline: There are no agents logged in to the BP.
Common Use Case:
Similar to the “Check BP Agents” Activity, this node provides more granular control on how to route interactions based upon Agent availability. If all agents are in a mix of unavailable and busy the call will follow the “All Busy” output leg. If all agents for that BP are offline, the call will follow the "All Offline" output leg.
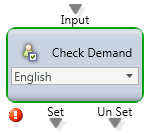
Check Demand
Media Type: All
Purpose: Used to make a routing decision if particular Agent Skills/Demands have been activated.
Output Legs:
- Set – the selected Demand is currently active.
- Un Set – the selected Demand is not currently active.
Common Use Case:
A check demand node can determine what demand/skill is currently active within the handling flow. It can then take action based on that demand, forwarding to a specific agent, BP or channel specific to that demand. When dealing with multiple demands/skills the “Check Demand” activity acts as a checkpoint to verify you are sending the interaction to the appropriate destination.
Check Schedule
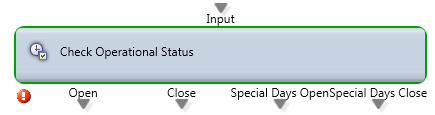
Check Operational Status
Media Type: All
Purpose: Routing decision that determines if the Contact Center or Channel or Business Process is currently open or closed based upon the defined Operating Hours and whether it is a “Special Day” (i.e. Holiday).
Output Legs:
- Open – When the time falls within the specified Operating Hours at the BP, Channel, or Organization level.
- Close – When the time falls outside the specified Operating Hours at the BP, Channel, or Organization level.
- Special Days Open – When the time falls within the specified Special Day hours at the BP, Channel or Organization level.
- Special Days Close – When the time falls outside the specified Special Day hours at the BP, Channel or Organization level. (Please see how to setup special days here)
Note:
The Operating Hours and Special Days can be defined at the Organization, Channel, or Business Process level. These hours are inherited down from the Organization to the Channel to the Business Process. If these hours are not defined at the BP level, the conditions will be taken from the Channel. If these hours not defined at the Channel level, the conditions will be taken from the Organization.
Tip: If your contact center is 24×7 the “from” and “to” times should be 12:00 AM and all days should be selected.
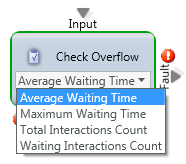
Check Overflow
Media Type: All
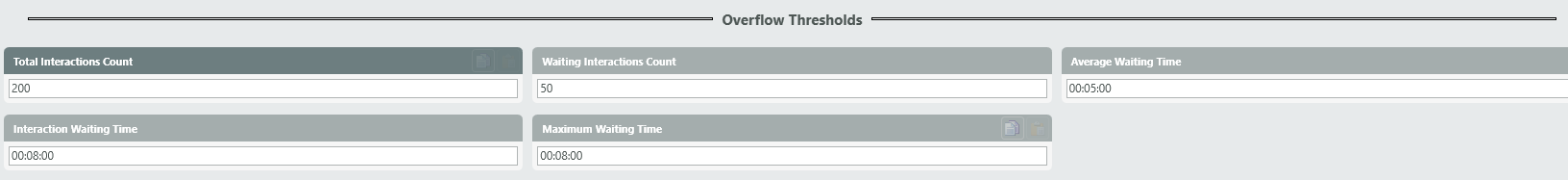
Purpose: Make routing decision based upon pre-defined Overflow thresholds set for the BP
Attributes: These attributes will trigger a “Yes” or “No” call path based on the values set on the “Handling Timeous” tab of the Business Process.
- Average Waiting Time
- Maximum Waiting Time
- Total Interactions Count
- Waiting Interactions Count
Output Legs:
- Yes – The specified threshold has been met.
- No – The specified threshold hat not been met.
Common Use Case:
The “Check Overflow” Activity is used to route Interactions that waited or are estimated to wait longer than desired. The Handing Timeouts are defined for each Business Process. Once the threshold is met, an Interaction is often routed to another Business Process, Channel, or 10-digit phone number.
Clear Assigned Agent
Media Type: All
Purpose: Removes any previously assigned agent from that interaction
Output Legs: N/A
Common Use Case:
This is used in conjunction with the “Assign Agent” and “Select Agent” Activities.
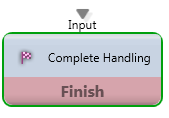
Complete Handling
Media Type: All
Purpose: Marks the end of an interaction and terminates any open connection.
Common Use Case:
When the flow will reaches this Activity, the interaction immediately ends. This node is also used as a final endpoint to terminate a successful interaction.
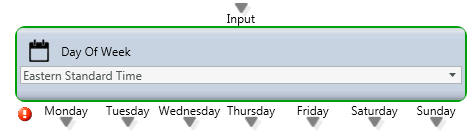
Day of Week
Media Type: All
Purpose: Routing decision based upon the day of week (and Time Zone)
Attributes: Time Zone
Output Legs:
- Monday
- Tuesday
- Wednesday
- Thursday
- Friday
- Saturday
- Sunday
Common Use Case:
Route interactions based upon the day of the week regardless of the current time.
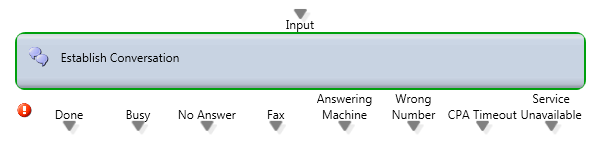
Establish Conversation
Media Type: Outbound Voice
Purpose: Generates an outbound call and route it based upon the connection status (answer, fax, answering machine, busy, etc.)
Output Legs:
- Done – Successfully connected to a live caller.
- Busy – Busy signal was encountered.
- No Answer – The call was not connected.
- Fax – Fax tone was encountered.
- Answering Machine – An Answering machine or Voicemail answered.
- Wrong Number – Get an error when dialing the contact which means that the dialed number is wrong and cannot be dialed
- CPA Timeout – The Call Progress Analysis used to determine if the call is a live call or a VM but no voice was detected (dead air) so after 10 seconds the call will exit via the timeout leg
- Service Unavailable – Get an error when dialing the contact which means that the dialed number is correct but is temporary not in service. The system will redial these calls after a few hours
Common Use Case:
Establish conversation is used for outbound dialer call flows. Disposition Codes are often assigned to each Output for reporting purposes.
The flow can be configured to play a message or leave a voicemail through the use of the “Simple Play” Activity on the Answering Machine leg.
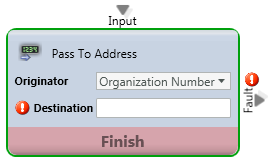
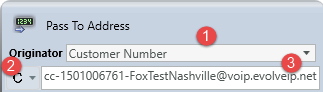
Pass to Address
Media Type: Telephony
Purpose: Forward the interaction to an internal or external number
Common Use Case:
Typically used send a caller to a 10-digit phone number.
Routing Calls to any BroadWorks (HPBX) Destination
The following configuration must be used when routing calls to a BroadWorks-based Call Center, Hunt Group, Auto Attendant or User.
Locate the User ID for the Call Center, Hunt Group, Auto Attendant or User via the Settings menu in OSSmosis.
Configure the Pass To Address activity within the Interaction Handling Flow
- Change Originator field to “Customer Number”
- Change Expression type from “P” to “C”
- Enter the User ID in the Destination field. Note: the User ID must end with @voip.evolveip.net
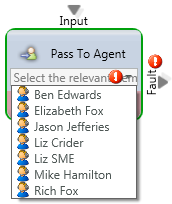
Pass to Agent
Media Type: All
Purpose: Route Interaction to a specific agent
Common Use Case:
This Activity is used to send the Interaction directly to a specific agent bypassing a queue.
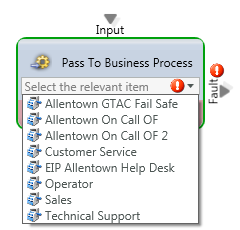
Pass to Business Process
Media Type: All
Purpose: Route Interaction to a different Business Process for handling
Attributes: List of all Business Processes.
Common Use Case:
To forward an Interaction to a particular business process either based upon a selection from a “Prompt and Collect Selection” Activity or specific queueing thresholds.
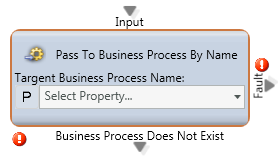
Pass to Business Process By Name
Media Type: All
Purpose: Forwards that interaction to a different Business Process for handling based upon a variable.
Attributes: This will reference a variable which is specified via the Customer Data upload from the application portal. The template for this data upload can be found via the ECS portal. Once you assign a number along with Business Process name you can then begin to configure the call flow to reference this variable.
Output Legs:
- Business Process Does Not Exist – There was no matching Business Process name.
Common Use Case:
Pass to Business Process by Name can route thousands of numbers dynamically in a single Activity through the use of the Customer Data upload to specify the Business Process associated with the number dialed (Destination DID) or originating from (Origin DID).
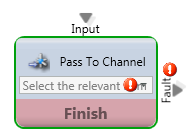
Pass to Channel
Media Type: All
Purpose: Forwards that interaction to a different channel for handling
Common Use Case:
This node would be used if you want to send the Interaction directly to another channel. This is commonly used to route to another menu structure.
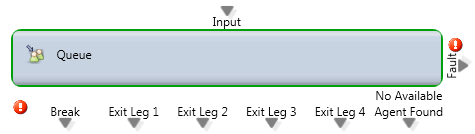
Queue
Media Type: All
Purpose: Queue Interaction for agent assignment with multiple sub-flows triggered based upon time elapsed.
The inside of this Activity will look different depending on the type of Routing Strategy assigned to the BP – Skill Based or Agent Idle Time (assigned in the “General” tab).
- Idle Time Strategy
- Time to Clear Assigned Agent – The desired time before clearing the agent who was preferred for this call through the use of the Assign Agent Activity)
- Exit Once Waiting Time Ends (Yes/No) – This is dependent on the value placed inside Maximum Waiting Time (See above “Check Overflow”)
- Threshold – Threshold timers before routing to specified Threshold Flows.
- First
- Second
- Third
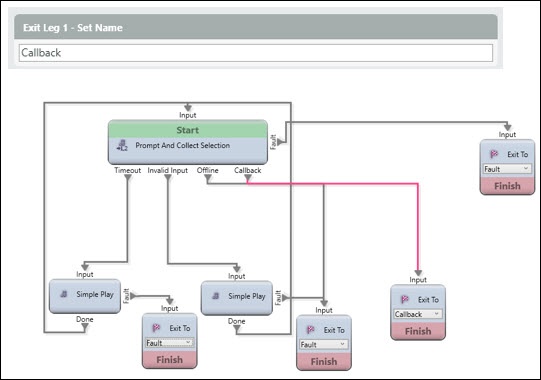
- Set Name – Exit Leg – The name of the Output Leg when leaving the Queue. This is commonly used in conjunction with “Prompt and Collect Selection” (i.e. the customer selects a Callback instead of continuing to wait in the queue)
- Leg 1
- Leg 2
- Leg 3
- Leg 4
- Threshold – Threshold timers before routing to specified Threshold Flows.
- Ignore Subflows For Offline Interactions (Idle) – An offline interaction, in most cases this option is checked by default
- Skill Based Strategy
- All other configurable fields remain the same
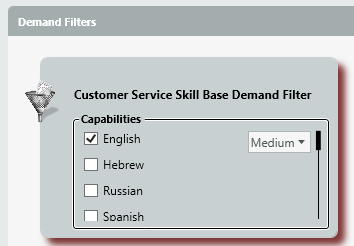
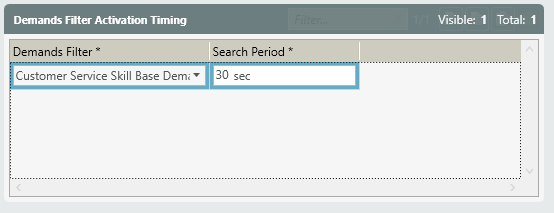
- Added setting of Demand Filter Activation Timing
- Demand Filters are defined on the “General” tab.
- This demand filter will now be available and you can specify how long you want to search for a particular demand filter and skill level.
Common Use Case:
The Queue node is the preferred method of routing calls to agents. Multiple Threshold Flows allow the customer’s experience to change as they wait by activating different routing treatments over time such as a Callback or Voicemail or an Overflow. The Queue also allows for true agent skilling by setting target Demand Filters and Search Periods to relax each skill requirement as the Interaction waits.
NOTE: Once an interaction reaches the last activity in the Interaction Handling Flow, it will return to the Start activity and route through the same activities again.
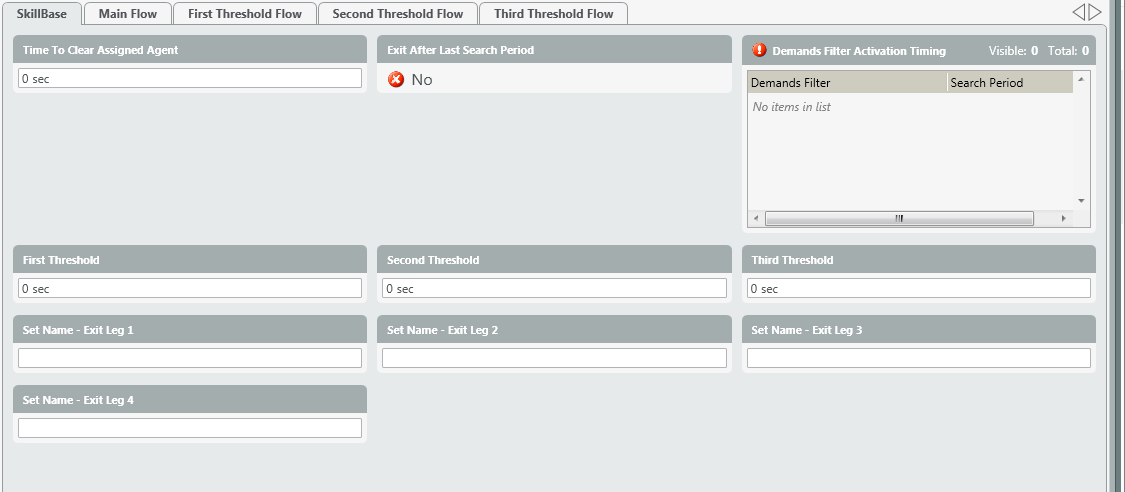
Inside View of Node: Skill Base
- Time to Clear Assigned Agent –
- Exit After Last Search Period (Yes/No) –
- Demands Filter Activation Timing –
- Threshold
- First
- Second
- Third
- Set Name – Exit Leg
- Leg 1
- Leg 2
- Leg 3
- Leg 4
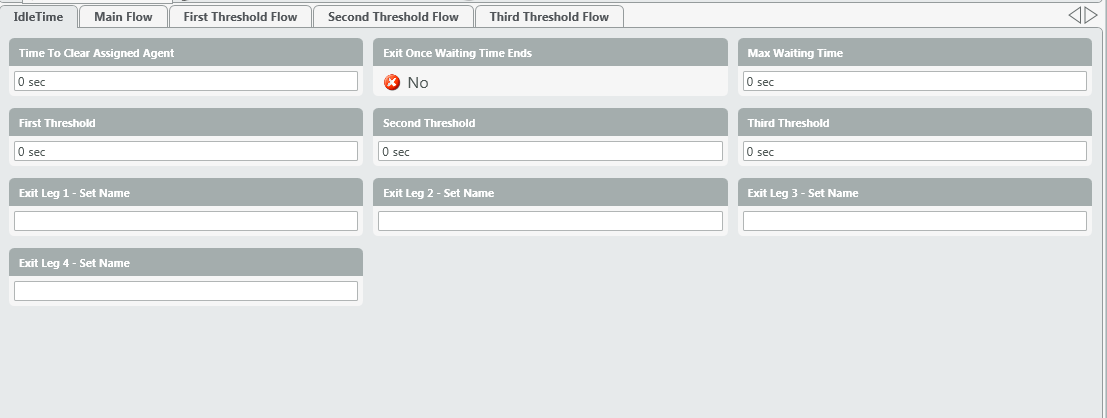
Inside View of Node: Agent Idle Time
- Time to Clear Assigned Agent
- Exit Once Waiting Time Ends (Yes/No) –
- Max Waiting Time
- Threshold
- First
- Second
- Third
- Exit Leg
- Leg 1
- Leg 2
- Leg 3
- Leg 4
Repeat for Each
This node is no longer in use.
Inside View of Node
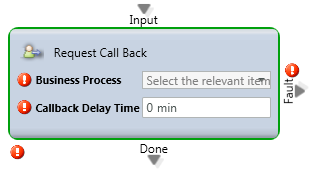
Request Call Back
Media Type: Voice
Purpose: Creates a Call Back Interaction where the system delivers an inbound Interaction to the Agent which is an Outbound Call to the party that requested it.
Attributes:
- List of Business Processes
- Callback Delay Time
Common Use Case:
For any type of callback this node is necessary to initiate that Interaction into the Queue. The callback delay time serves as the initial timeframe in which the call will be re-presented back into queue (additional callback information).
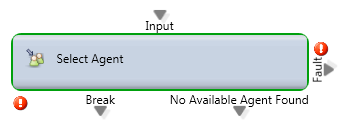
Select Agent
Media Type: All
Purpose: This selects the best agent to handle the interaction and defines the queue experience for that customer. This Activity has been replaced by the Queue activity and should only be used in rare instances.
Output Legs:
- Break: This call path will only be triggered if the “Exit To” node in the subflow is pointed to “Break”.
- No Available Agent Found: This will trigger should the “Exit Once Waiting Time Ends” is set to Yes and the configured “Max Waiting Time” is exceeded.
Common Use Case:
Select agent will be used if you want to route a call to a specific agent. Possibly the agent who last spoke with that caller or one that is proficient for that particular customer (with the inclusion of “Assign Agent”) The select agent node can be configured to exit after a maximum waiting time or within the subflow of the node. Upon exiting best practice is for the caller to either be directed into voicemail or to the queue node to be answered.